
More Protein Performance - vs. More Grams of Protein


Clinically Proven to Optimize Protein Performance
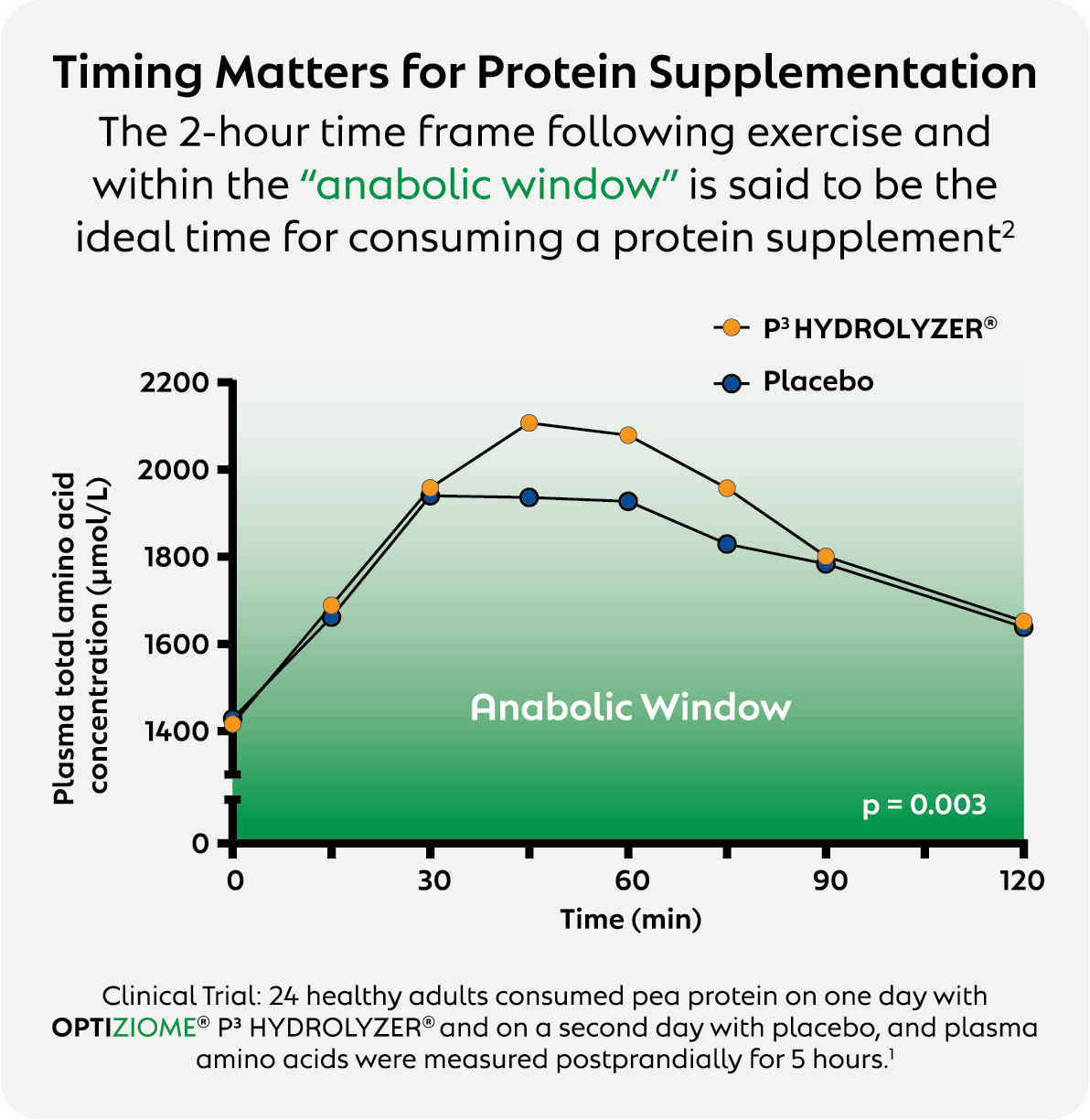
Timing Matters for Protein Supplementation
The 2-hour time frame following exercise and within the “anabolic window” is said to be the ideal time for consuming a protein supplement¹
For Many Different Lifestyles and Life Stages

Sports Nutrition – Build Muscle

Active Nutrition – Muscle Recovery

Healthy Aging – Maintain Muscle
Added Consumer Benefits
Let BIO-CAT help you with your application opportunities!

References:
*These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
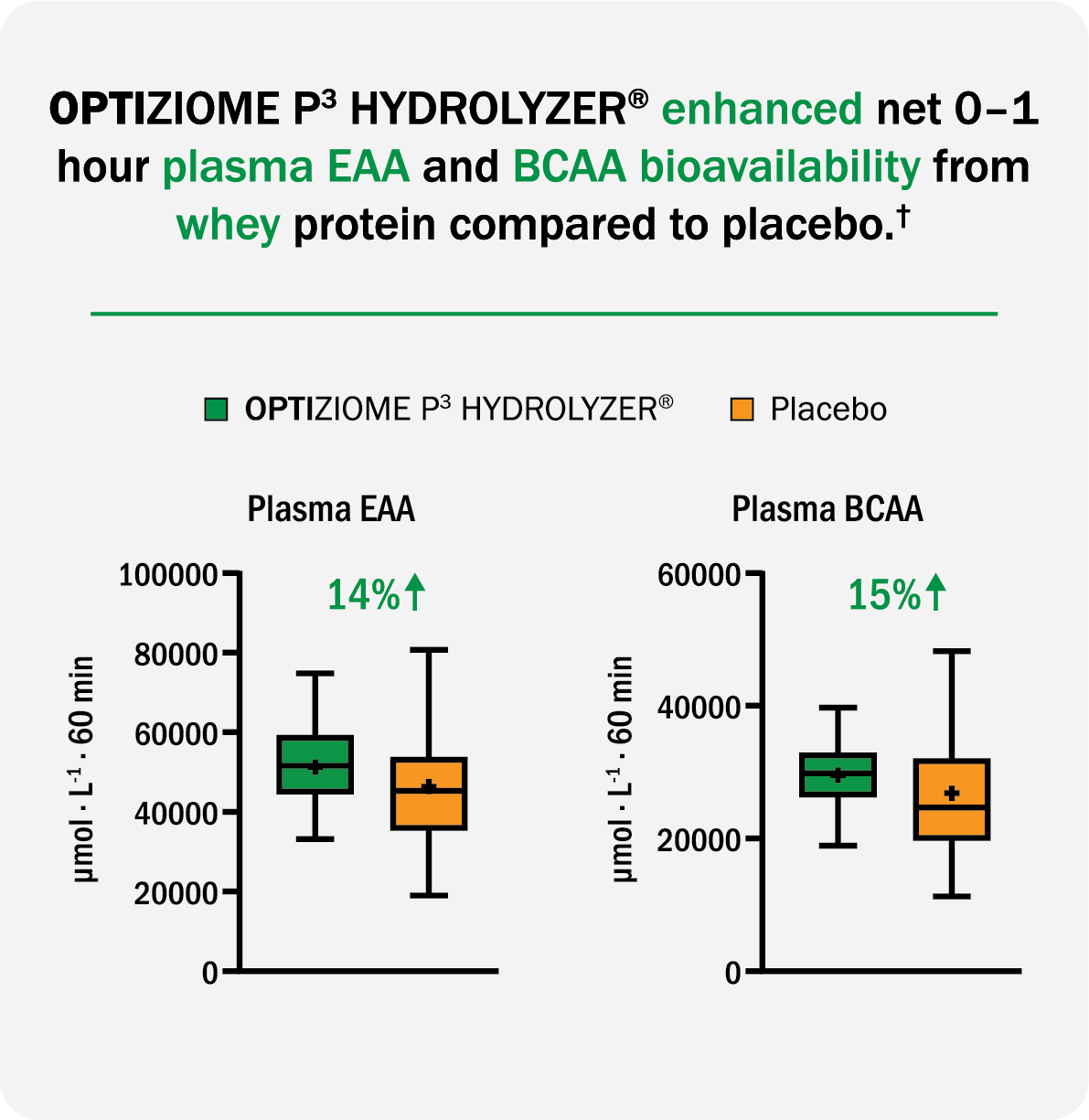
†Huang, Yijia, … Churchward-Venne, Tyler A. (2025). Acute effects of oral microbial protease co-ingestion with whey protein on postprandial plasma amino acid concentrations, appetite, and satiety in healthy adults: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover clinical trial. The Journal of Nutrition, Volume 0, Issue
BCAAs = Branched Chain Amino Acids
¹Kerksick CM, Arent S, Schoenfeld BJ, et al. International society of sports nutrition position stand: nutrient timing. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2017;14:33.
²Paulussen, K. J. M., Askow, A. T., Deutz, M. T., et al. (2024). Acute Microbial Protease Supplementation Increases Net Postprandial Plasma Amino Acid Concentrations after Pea Protein Ingestion in Healthy Adults: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. The Journal of Nutrition (published online, in press). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tjnut.2024.03.009

