What Are FODMAPs?
Some fibers are categorized as FODMAPs (fermentable oligosaccharide, disaccharide, monosaccharides and polyols), which are associated with GI symptoms in certain individuals. FODMAP foods include many legumes, beans, vegetables, fruits, and wheat.
Gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms such as abdominal bloating and intestinal gas are influenced by dietary factors, including nondigestible carbohydrates (dietary fibers)2.
Dietary fiber is generally healthy3, but not all fibers are alike. Some individuals report increased GI symptoms after consuming dietary fiber4.
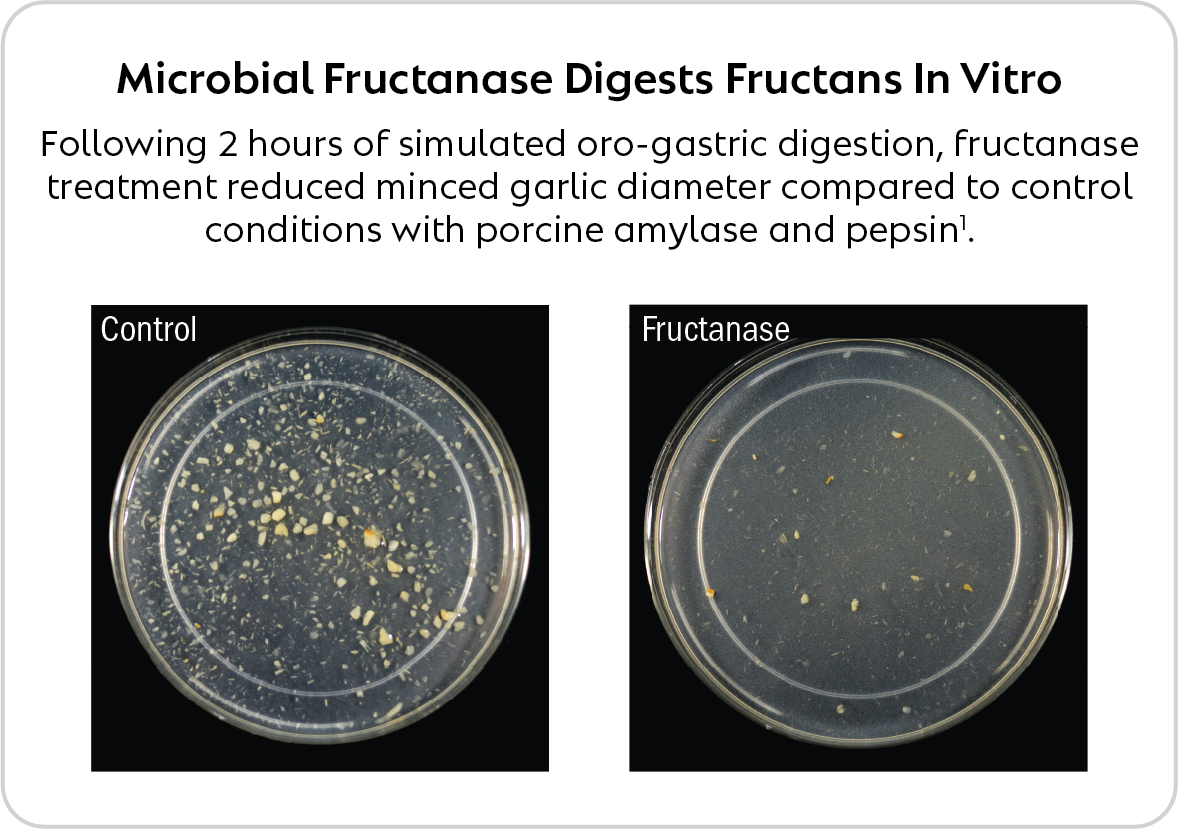
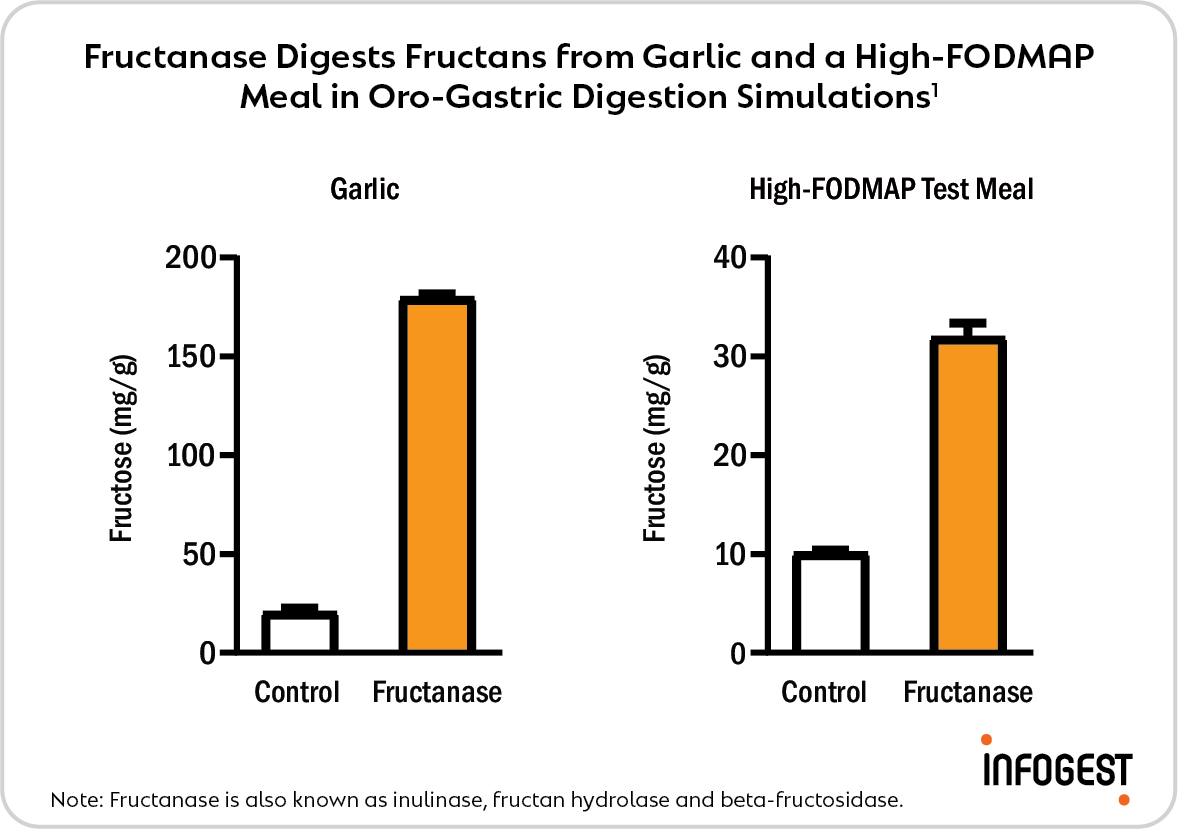
BIO-CAT has developed a food-grade microbial fructanase into a novel dietary supplement ingredient to target fructan-type FODMAPs and help support digestive health*.

In Vitro Data for OPTIZIOME® Fructanase
References:
*These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
1Guice, J. L., et al. (2023). Microbial Inulinase Promotes Fructan Hydrolysis Under Simulated Gastric Conditions. Frontiers in Nutrition, 10, 1129329.
2Fernández-Bañares F. (2022). Carbohydrate Maldigestion and Intolerance. Nutrients, 14, 1923.
3Shivakoti, R., et al. (2022). Intake and Sources of Dietary Fiber, Inflammation, and Cardiovascular Disease in Older US Adults. JAMA Network Open, 5, e225012.
4Peng, A. W., et al. (2019). Effects of the DASH Diet and Sodium Intake on Bloating: Results From the DASH-Sodium Trial. The American Journal of Gastroenterology, 114, 1109–1115.
5 Garvey, S. M., … Baisley, J. (2024). Safety and Tolerability of Microbial Inulinase Supplementation in Healthy Adults: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Gastro Hep Advances, 3, 920–930.




